Contents
2. Procedure and control description
A customer creates orders based on the order list and the product list.
2. Procedure and control description
These orders trigger a production order in production control. If you link the customer object directly to a supermarket (information connection), the products are taken directly from the supermarket.
Three different cases are considered with regard to order generation:
•Demand by cycle times: According to this setting, the due date for delivery per order is independent of each other.
oEvery 1 hour once Product A order is triggered.
oEvery 2 hours once Product B order is triggered.
oEvery 2nd hour there will be a overlap of order trigger of both Product A & Product B.

Figure 1 - Order mode: Demand by cycle times
•Consecutively by products: The orders are processed one after the other according to this setting. If delays occur for the current order, the subsequent orders are also delayed.
oAccording to these settings 30 parts of Product A will be requested after 1 hour, then 15 parts of Product B will be requested after 2 hours.
oAfter that 30 parts of Product A will be requested after another 1 hour, and so on.
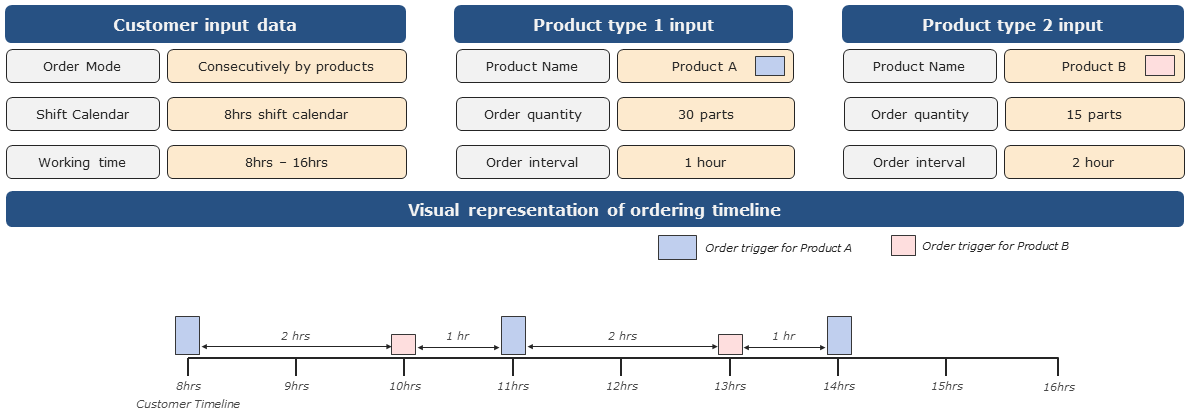
Figure 2 - Order mode: Consecutively by products
•Order Mode: Demand by cycle time with variation
oEvery 1 hour once Product A order is triggered.
oThere is a variation in order, instead of a constant order trigger of 30 products.
oVariation ranges from 27 to 33 products per hour and this is completely a random trigger.
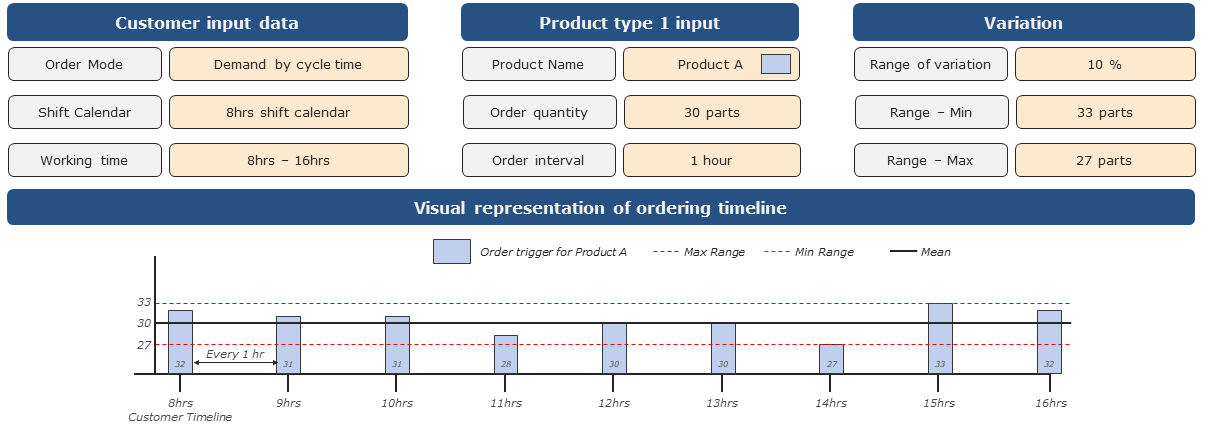
Figure 3 - Order Mode: Demand by cycle time with variation
Customer orders depending on shift calendar
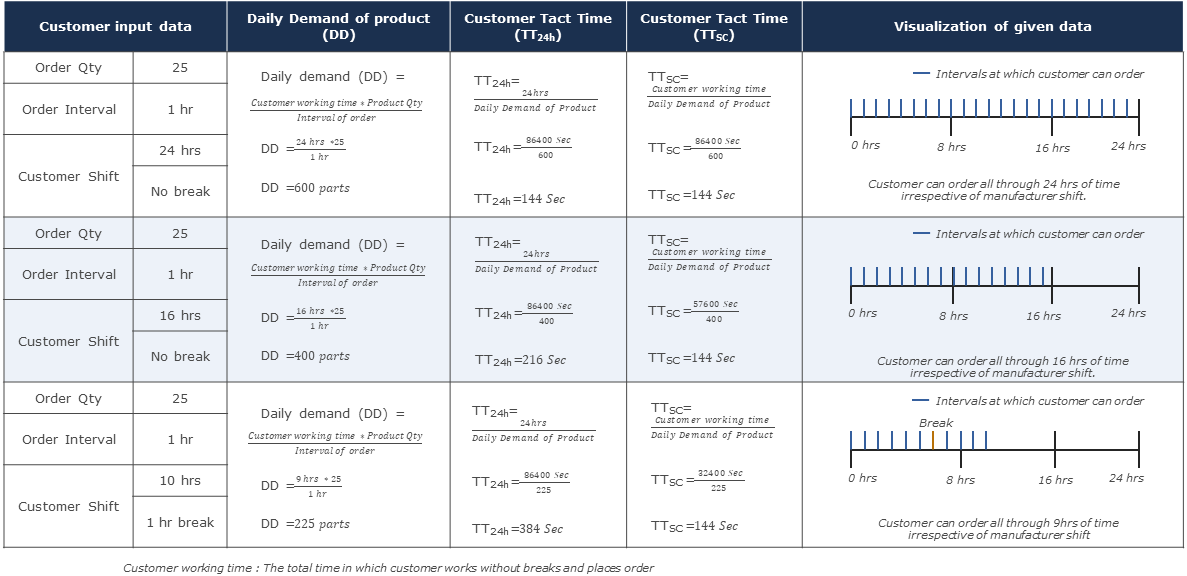
Figure 4 - Customer orders depending on shift calendar
Customer and Process - Impact of shift calendar and order backlogs
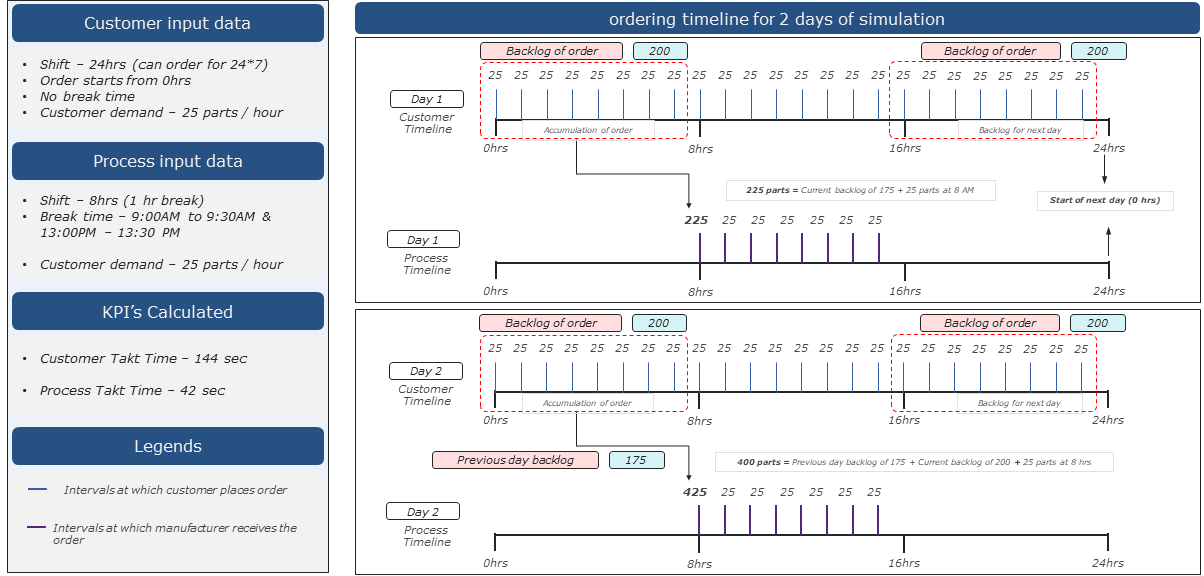
Figure 5 - Customer and Process - Impact of shift calendar and order backlogs
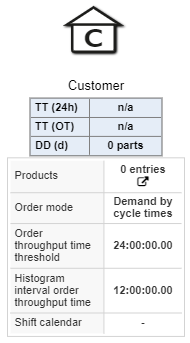
Figure 6 - Customer |
|
See chapter Possible connections to objects.
© SimPlan AG - Hanau District Court, Commercial Register (Part B) 6845 - info@simplan.de - www.simplan.de/en